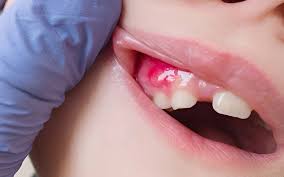
Tooth infections, often stemming from untreated cavities, gum disease, or trauma, can lead to serious health complications if not addressed promptly. While it’s uncommon for a tooth infection to be fatal, understanding the potential risks and timelines associated with untreated infections is crucial. In this article, we’ll explore How Long Until a Tooth Infection Kills You, how they can affect your health, the signs to watch for, and the importance of seeking timely treatment.
Understanding Tooth Infections
What Is a Tooth Infection?
A tooth infection, also known as a dental abscess, occurs when bacteria invade the tooth’s pulp—the innermost part of the tooth containing nerves and blood vessels. This invasion often results from untreated cavities, cracked teeth, or gum disease. The infection can spread from the tooth to surrounding tissues and even to other parts of the body if left untreated.
Types of Tooth Infections
There are generally three types of dental abscesses:
- Periapical Abscess: This type occurs at the tip of the tooth root and is usually a result of untreated dental decay or trauma.
- Periodontal Abscess: This type forms in the gums adjacent to a tooth root, often due to gum disease.
- Gingival Abscess: This infection is located in the gum tissue itself, typically resulting from a foreign object or injury.
Symptoms of a Tooth Infection
Recognizing the symptoms of a tooth infection is essential for seeking timely treatment. Common signs include:
- Severe Toothache: A persistent and throbbing pain that may worsen when lying down.
- Swelling: Swelling of the gums, face, or jaw.
- Redness and Warmth: Infected areas may appear red and feel warm to the touch.
- Pus or Discharge: Pus may ooze from the affected area, indicating the presence of infection.
- Fever: An elevated temperature can signal that the body is fighting an infection.
- Bad Breath: Foul-smelling breath often accompanies dental infections.
- Difficulty Swallowing or Breathing: In severe cases, the swelling can obstruct airways or make swallowing difficult.
If you experience any of these symptoms, especially severe pain or swelling, it’s essential to consult a dental professional immediately.
How Tooth Infections Can Become Life-Threatening
While most tooth infections can be treated effectively, there are scenarios where they can lead to severe complications, including:
1. Spread of Infection
If untreated, the infection can spread from the tooth to nearby tissues and structures. It may travel to the jaw, neck, or even the brain, leading to serious health risks. Conditions such as cellulitis (a skin infection) or cavernous sinus thrombosis (a blood clot in the brain) can occur, both of which are potentially life-threatening.
2. Sepsis
Sepsis is a severe response to infection that can result in systemic inflammation throughout the body. Tooth infections can lead to sepsis if the bacteria enter the bloodstream. Sepsis can cause organ failure and death if not treated immediately.
3. Osteomyelitis
This is a bone infection that can occur when bacteria spread from a tooth infection to the jawbone. Osteomyelitis can be challenging to treat and may require prolonged antibiotic therapy or surgery.
How Long Until a Tooth Infection Kills You?
The timeline for how long a tooth infection might become fatal varies greatly depending on several factors:
- Overall Health: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with chronic illnesses, are at higher risk of complications from infections.
- Severity of the Infection: A mild infection may take longer to develop severe complications than a more aggressive infection.
- Timeliness of Treatment: The sooner a tooth infection is treated, the lower the risk of serious complications. Immediate dental care can often prevent life-threatening situations.
General Timeline
While it’s difficult to predict an exact timeline, here’s a rough guideline based on typical progression:
- Within Hours to Days: Symptoms can develop rapidly. Within a few days, an untreated tooth infection can worsen, leading to increased pain, swelling, and systemic symptoms like fever.
- Within Days to Weeks: If left untreated, the infection may spread to surrounding tissues or into the bloodstream. Severe symptoms could manifest, including difficulty breathing or swallowing.
- Weeks to Months: In severe cases, if treatment is not sought, the risk of life-threatening complications, such as sepsis or osteomyelitis, increases. These conditions can be fatal if not addressed promptly.
Importance of Seeking Treatment
Immediate Dental Care
If you suspect you have a tooth infection, seeking dental care as soon as possible is crucial. A dentist will typically:
- Perform a thorough examination and possibly take X-rays to assess the extent of the infection.
- Drain any abscess to relieve pressure and remove pus.
- Prescribe antibiotics to eliminate the bacterial infection.
- Discuss options for treating the underlying cause, such as filling a cavity or performing a root canal.
Preventative Measures
Taking preventive steps can significantly reduce the risk of tooth infections:
- Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Regular brushing and flossing help prevent cavities and gum disease.
- Regular Dental Checkups: Visit your dentist for routine checkups and cleanings to catch issues early.
- Avoid Tobacco and Limit Alcohol: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can weaken your immune system and increase infection risk.
Conclusion
While the prospect of a tooth infection becoming life-threatening is concerning, it’s important to remember that timely treatment can prevent most serious complications. If you experience symptoms of a tooth infection, don’t delay seeking care. With proper attention and care, you can effectively manage a tooth infection and maintain your overall health.
In summary, understanding how long until a tooth infection kills you involves recognizing the signs of infection, understanding the risks associated with untreated conditions, and seeking prompt dental treatment. By being proactive about your oral health, you can significantly reduce your risk of severe complications and enjoy a healthier, pain-free life.